Page 33 - 10.Sayı
P. 33
31
2024 سكفوس ةخسن - ريه سنفيد
336 THE MILITARY BALANCE 2024
Increase In addition to the establishment of
Iraq* JODDB, Jordan created a dedicated free
USD10.36bn
zone for defense industries. This strategic
move aimed to foster growth in the de-
fense sector by providing tax incentives,
Algeria
USD18.31bn
essential infrastructure, and high-level
security for defense-related companies.
The free zone has been instrumental in
Qatar
εUSD9.02bn attracting both local and international
Saudi Arabia* defense firms, facilitating the growth of
Mauritania USD69.07bn
USD0.24bn
Jordan’s defense manufacturing capabil-
ities.
Israel Morocco
USD22.48bn UAE
εUSD20.74bn USD6.49bn
Oman By 2022, JODDB had significantly expand-
USD6.51bn Iran*
εUSD7.41bn Tunisia ed its production portfolio, boasting 80
USD1.25bn
Kuwait Jordan different defense products and exporting
Bahrain USD2.25bn
USD1.41bn USD7.77bn Egypt
USD4.88bn them to 37 countries. Some of its notable
Decrease Lebanon Libya Palestinian Authority Syria Yemen * Security expenditure removed from defence budget gure. Iran conversion using achievements include the production of
n.k
n.k
n.k
n.k
n.k
NIMA exchange rate.
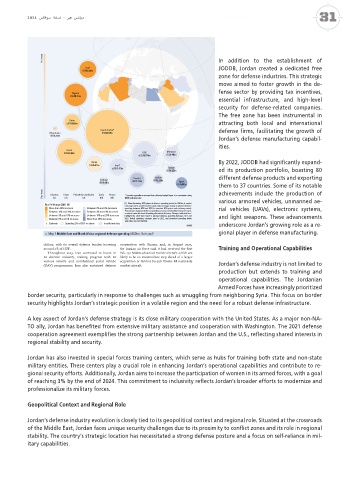
[1] Map illustrating 2023 planned defence-spending levels (in USDbn at market various armored vehicles, unmanned ae-
Real % Change (2022–23) exchange rates), as well as the annual real percentage change in planned defence
More than 20% increase Between 0% and 3% decrease spending between 2022 and 2023 (at constant 2015 prices and exchange rates). rial vehicles (UAVs), electronic systems,
Between 10% and 20% increase Between 3% and 10% decrease Percentage changes in defence spending can vary considerably from year to year,
as states revise the level of funding allocated to defence. Changes indicated here
Between 3% and 10% increase Between 10% and 20% decrease highlight the short-term trend in planned defence spending between 2022 and and light weapons. These advancements
Between 0% and 3% increase More than 20% decrease 2023. Actual spending changes prior to 2022, and projected spending levels
post-2023, are not re ected.
ε Estimate Spending 2% of GDP or above Insuf cient data underscore Jordan’s growing role as a re-
©IISS
ɺ Map 7 Middle East and North Africa: regional defence spending (USDbn, %ch yoy) 1 gional player in defense manufacturing.
ǰȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ǰȱ ǰȱ ȱ ȱ ŬŪŬŭǰȱ
ȱŬƖȱȱ ǯȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ęȱ Training and Operational Capabilities
ȱ ŬŪŬŭǰȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȬūŭŪȱ Ĵȱȱȱǰȱ ȱȱ
ȱ ȱ ¢ǰȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ¢ȱȱȱȱȱȱȱȱȱȱ
ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱȱ ȱ Ȭŭů ȱFlanker ȱȬȱ
ǻ Ǽȱ ǯȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱ ȱǯ Jordan’s defense industry is not limited to
production but extends to training and
operational capabilities. The Jordanian
Armed Forces have increasingly prioritized
border security, particularly in response to challenges such as smuggling from neighboring Syria. This focus on border
security highlights Jordan’s strategic position in a volatile region and the need for a robust defense infrastructure.
A key aspect of Jordan’s defense strategy is its close military cooperation with the United States. As a major non-NA-
TO ally, Jordan has benefited from extensive military assistance and cooperation with Washington. The 2021 defense
cooperation agreement exemplifies the strong partnership between Jordan and the U.S., reflecting shared interests in
regional stability and security.
Jordan has also invested in special forces training centers, which serve as hubs for training both state and non-state
military entities. These centers play a crucial role in enhancing Jordan’s operational capabilities and contribute to re-
gional security efforts. Additionally, Jordan aims to increase the participation of women in its armed forces, with a goal
of reaching 3% by the end of 2024. This commitment to inclusivity reflects Jordan’s broader efforts to modernize and
professionalize its military forces.
Geopolitical Context and Regional Role
Jordan’s defense industry evolution is closely tied to its geopolitical context and regional role. Situated at the crossroads
of the Middle East, Jordan faces unique security challenges due to its proximity to conflict zones and its role in regional
stability. The country’s strategic location has necessitated a strong defense posture and a focus on self-reliance in mil-
itary capabilities.