Page 33 - 11.Sayı
P. 33
Real global defence spending changes by region 2021–23
*
40
35
2021
30
2022
25
2023
20
15
%
10
5
0
-5
-10
Sub-Saharan
Middle East and
Asia
Russia and
North America
Europe
Latin America
Global
Eurasia
Africa
and the
North Africa
Caribbean
Impact of in ation on global defence expenditure 2015–23
2.3
2.2
2.1
2.0
USDtrn
1.9
1.8
1.7
Current/Nominal, USDtrn
1.6
Constant/Real, 2015 USDtrn
1.5 * Excludes states for which insuf cient data is available Defence and military analysis: Defence budgets and expenditure 15
2018
2015 2016 2024 ناريطلل رصم ضرعم ةخسن - ريه نفيد 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 31
2017
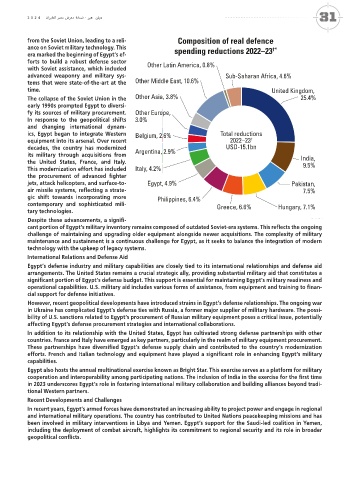
Composition of real defence Composition of real defence
from the Soviet Union, leading to a reli-
ance on Soviet military technology. This
spending increases 2022–23 †* spending reductions 2022–23 †*
era marked the beginning of Egypt’s ef-
Sub-Saharan Africa, 1.6% forts to build a robust defense sector Other Latin America, 0.8%
Latin America &
with Soviet assistance, which included
the Caribbean, 1.0%
Other North America, 0.4% advanced weaponry and military sys- Sub-Saharan Africa, 4.6%
tems that were state-of-the-art at the Other Middle East, 10.6%
Other Eurasia, 1.1% time. United States, United Kingdom,
Other Middle The collapse of the Soviet Union in the Other Asia, 3.8% 25.4%
22.2%
East, 3.7% early 1990s prompted Egypt to diversi-
Other Asia, 4.9% fy its sources of military procurement. Other Europe,
In response to the geopolitical shifts 3.0%
Other Europe, and changing international dynam-
7.1% Total increases Belgium, 2.6% Total reductions
ics, Egypt began to integrate Western
2022–23 †
Spain, 2.1% equipment into its arsenal. Over recent 2022–23 †
China,
decades, the country has modernized Argentina, 2.9% USD-15.1bn
USD128bn
10.2%
Taiwan, 2.4% its military through acquisitions from India,
the United States, France, and Italy.
Japan, 2.6% This modernization effort has included Italy, 4.2% 9.5%
Ukraine,
Germany, 3.7% the procurement of advanced fighter
8.9%
jets, attack helicopters, and surface-to- Egypt, 4.9% Pakistan,
Poland, 4.3% air missile systems, reflecting a strate- 7.5%
Algeria, 5.3% gic shift towards incorporating more Philippines, 6.4%
contemporary and sophisticated mili-
Russia, 18.6% Greece, 6.6% Hungary, 7.1%
tary technologies.
Despite these advancements, a signifi- ©IISS
cant portion of Egypt’s military inventory remains composed of outdated Soviet-era systems. This reflects the ongoing
† At constant 2015 prices and exchange rates challenge of maintaining and upgrading older equipment alongside newer acquisitions. The complexity of military
maintenance and sustainment is a continuous challenge for Egypt, as it seeks to balance the integration of modern
* Analysis only includes countries for which sufficient comparable data is available. Notable exceptions include Cuba, Eritrea, Libya, North Korea, Syria and Venezuela.
technology with the upkeep of legacy systems.
International Relations and Defense Aid
Egypt’s defense industry and military capabilities are closely tied to its international relationships and defense aid
arrangements. The United States remains a crucial strategic ally, providing substantial military aid that constitutes a
significant portion of Egypt’s defense budget. This support is essential for maintaining Egypt’s military readiness and
operational capabilities. U.S. military aid includes various forms of assistance, from equipment and training to finan-
cial support for defense initiatives.
However, recent geopolitical developments have introduced strains in Egypt’s defense relationships. The ongoing war
in Ukraine has complicated Egypt’s defense ties with Russia, a former major supplier of military hardware. The possi-
bility of U.S. sanctions related to Egypt’s procurement of Russian military equipment poses a critical issue, potentially
affecting Egypt’s defense procurement strategies and international collaborations.
In addition to its relationship with the United States, Egypt has cultivated strong defense partnerships with other
countries. France and Italy have emerged as key partners, particularly in the realm of military equipment procurement.
These partnerships have diversified Egypt’s defense supply chain and contributed to the country’s modernization
efforts. French and Italian technology and equipment have played a significant role in enhancing Egypt’s military
capabilities.
Egypt also hosts the annual multinational exercise known as Bright Star. This exercise serves as a platform for military
cooperation and interoperability among participating nations. The inclusion of India in the exercise for the first time
in 2023 underscores Egypt’s role in fostering international military collaboration and building alliances beyond tradi-
tional Western partners.
Recent Developments and Challenges
In recent years, Egypt’s armed forces have demonstrated an increasing ability to project power and engage in regional
and international military operations. The country has contributed to United Nations peacekeeping missions and has
been involved in military interventions in Libya and Yemen. Egypt’s support for the Saudi-led coalition in Yemen,
including the deployment of combat aircraft, highlights its commitment to regional security and its role in broader
geopolitical conflicts.